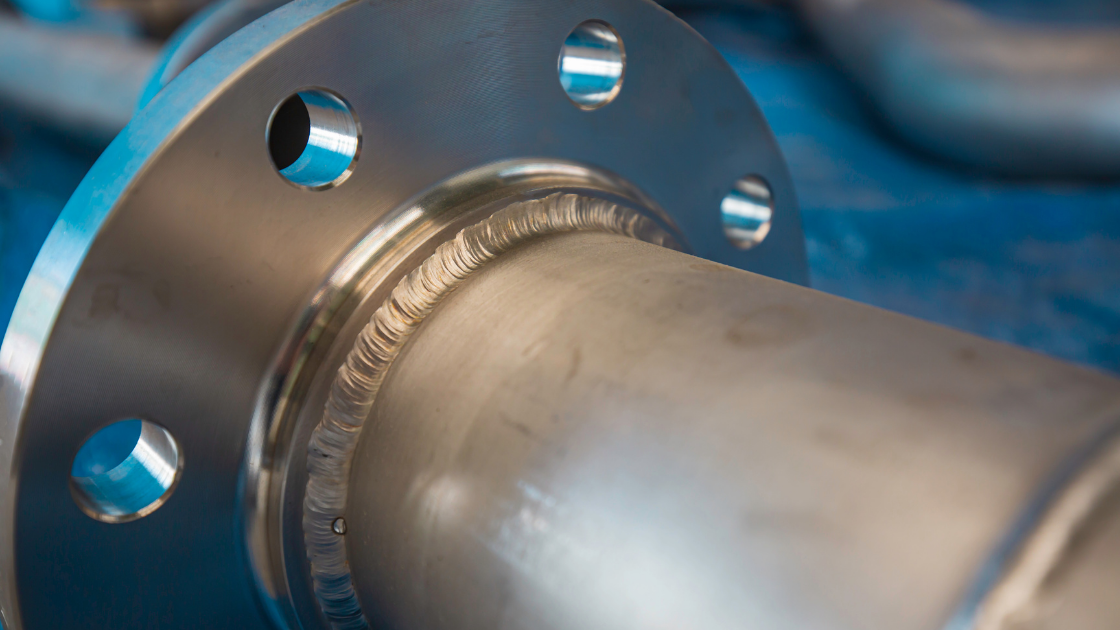

Classes of stainless steel are organized by their crystalline structure, which describes how their atoms are arranged. Of the five classes of stainless steel—martensitic, ferritic, austenitic, duplex, and precipitation-hardening—austenitic is the most common. The grades in this group contain high chromium and nickel content which provides good corrosion resistance and desirable mechanical properties. Read on to learn everything you need to know about austenitic stainless steels.
Kloeckner Metals is a full-line stainless steel supplier and service center. Download our stainless steel spec sheet and check what Kloeckner Metals routinely stocks.
Austenitic stainless steels possess an austenitic microstructure, meaning their cells are in the shape of a cube with one atom at the corner of each cube and one in the middle. In crystallography, this is known as a face-centered crystal structure.
Stainless steel becomes austenitic by alloying steel with enough nickel, nitrogen, and/or manganese to keep the microstructure at all temperature ranges, from very low to the melting point. Since they possess the same microstructures at all temperatures, they are not hardenable by heat treatment. However, they can be hardened through cold-working. In addition, grades in this class are non-magnetic.
Some of the major advantages of austenitic stainless steels include:
They are divided into two subgroups: the 200 and 300 series. In 300 series stainless steel, nickel is the most prominent alloying element. In 200 series stainless steel, manganese and nitrogen are the leading alloying elements, though it does still contain some nickel.
The 300 series is more common because it has a wider range of applications. The high content of nickel it has gives 300 series of austenitic stainless steel superior corrosion resistance. Although 200 series stainless steels have a narrower range of applications, it is still utilized in various items due to its high impact resistance and toughness. Some uses for 200 series stainless steel include:
300 series stainless steel is the larger subgroup and has a much wider range of applications than the 200 series. The most common austenitic stainless-steel grades are from the 300 series.
Not only is it the most popular type of austenitic stainless steel, 304 is the most common type of stainless steel. With high content of nickel and chromium, this grade possesses a desirable combination of strength, corrosion resistance, and fabricability.
As the second most used grade of stainless steel, 316 is very similar to 304. However, the addition of Molybdenum gives it an increased resistance to corrosion and higher heat resistance.
This grade has a high chromium and medium nickel content that makes it highly resistant to oxidation and corrosion. It is used for high temperature applications.
Titanium is added to this grade as well as a large amount of carbon, which gives it an increased amount corrosion resistance when exposed to chemicals at high temperatures.
Another differing characteristic of austenitic stainless steel is their carbon content. The standard grades of austenitic stainless steel have no minimum carbon requirement, although they do have a maximum requirement of .08% carbon. Some grades of austenitic stainless steel such as 304 and 316 is offered in a high carbon grade or low carbon grade depending on the added capabilities you seek.
Low carbon grades also known as L grades are used to provide extra corrosion resistance. The carbon levels are kept at 0.03% or below to reduce corrosion after welding, which is caused by carbide precipitation.
High carbon grades contain a maximum of 0.10% carbon and a minimum of 0.04% carbon to help the stainless steel retain strength at higher temperatures. H grades can be used as standard grades as long as their carbon contents are 0.08% max. These grades are commonly used for applications that expose them to extreme temperature environments.
| Grade | C | Mn | Si | P | S | Cr | Mo | Ni | N | Ti |
| 304 | 0.08 | 2.0 | 0.75 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 18.0- 20.0 | – | 8.0- 10.5 | 0.10 | – |
| 316 | 0.08 | 2.00 | 0.75 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 16.00-18.00 | 2.00- 3.00 | 10.00-14.00 | 0.10 | – |
| 310 | 0.25 | 2.00 | 1.50 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 24.00- 26.00 | – | 19.00-22.00 | – | – |
| 321 | .08 | 2.00 | 0.75 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 17.0-19.0 | – | 9.0-12.0 | 0.10 | 0.70 |
|
Grade |
Tensile Strength (MPa) min. |
Tensile Strength (ksi) |
Elongation % (HB) max |
Hardness (Brinell) HB max |
|
304 |
515 |
74 |
40 |
201 |
|
316 |
515 |
74 |
40 |
217 |
|
310 |
520 |
75 |
40 |
217 |
|
321 |
515 |
74 |
40 |
217 |
They are the most popular class of stainless steel because of the key properties they possess. Their superior corrosion resistance, formability, strength, and heat resistance make them a staple in transport, industrial, and architectural products. In addition, austenitic stainless steel is used to the pharmaceutical, chemical, and food industries because its corrosion resistance provides high cleanability, low maintenance, and durability.
Known as the workhorse of steel for its durability and versatility, austenitic stainless steel is a staple in the metal industry. It has high formability, corrosion resistance, and heat resistance which makes it a good choice for many products.
Kloeckner Metals is a full-line stainless steel supplier and service center. Kloeckner Metals combines a national footprint with the latest fabrication and processing technologies and most innovative customer service solutions.

Steel base plates are fundamental elements employed in various manufacturing...
Metal fabrication is a critical process that transforms raw metal...
The solar industry has undergone a significant transformation by incorporating...
X
The Kloeckner Metals website uses modern technologies. Unfortunately, your browser doesn't support those technologies.
Download the latest version of one of these browsers to experience the site: