Before we can answer what is plasma cutting, we have to start with the question, what is plasma? It turns out that there are more than three states of matter—solid, liquid, and gas. There’s also a fourth: plasma. Matter moves from state to state when energy is added to the material. Ice becomes water when you add heat. Add more heat and it becomes water vapor. Add even more heat, enough that the gas becomes separated into ions and can conduct electricity, it becomes plasma.
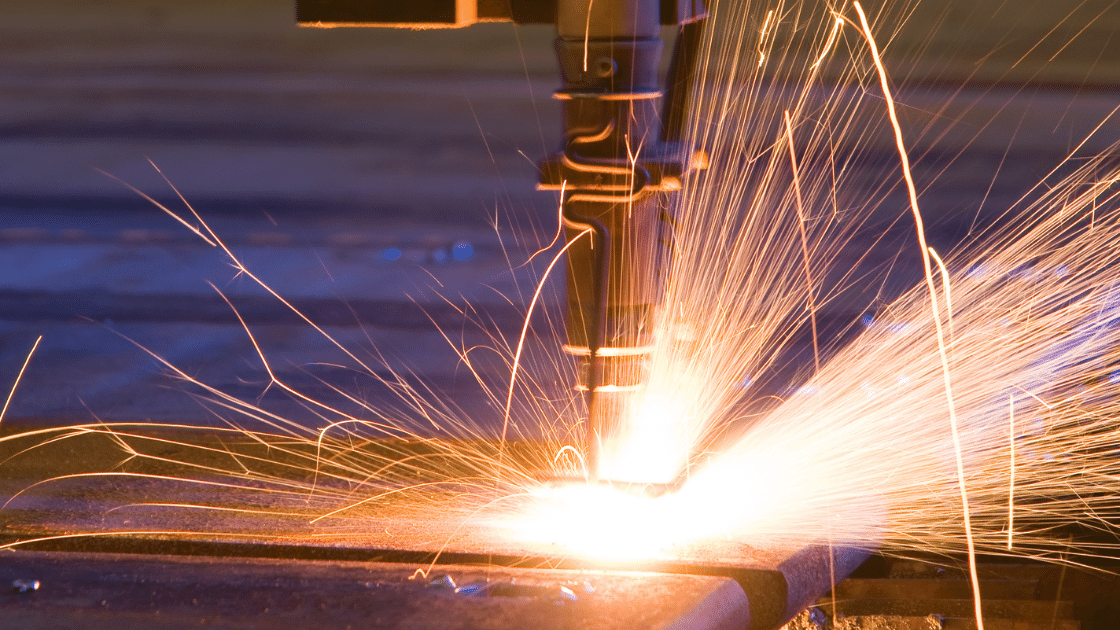
Plasma cutting, otherwise known as plasma arc cutting, is a type of melting process where a jet of 20,000°C+ ionized gas melts and expels the material that is cut away from the metal. The process is also known as plasma arc cutting because it involves an electric arc striking between the electrode (the cathode) and the material (the anode). The electrode sits in a water- or air-cooled gas nozzle, working by restricting the arc and causing the formation of the high-temperature, high-velocity plasma jet.
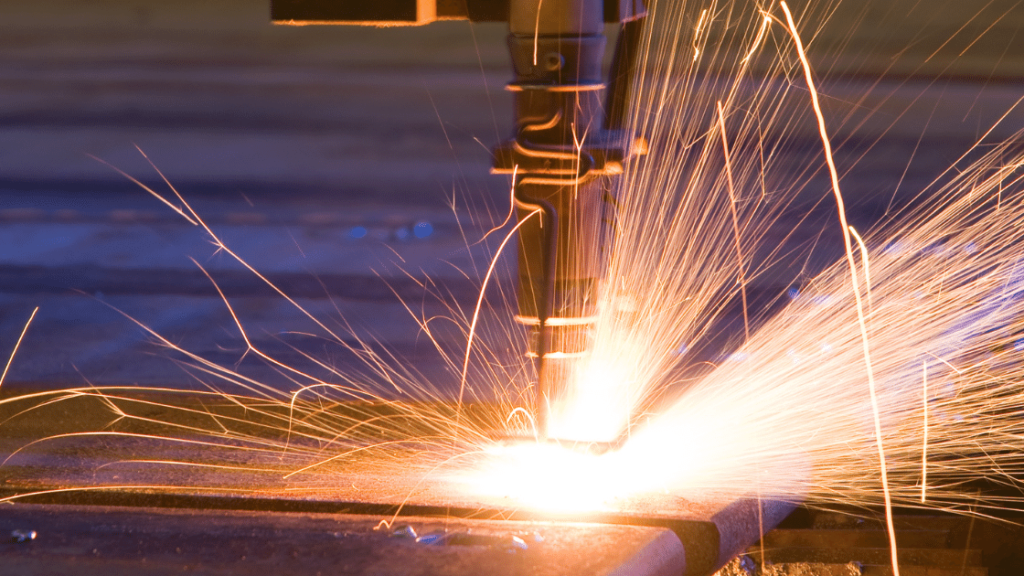

When the plasma jet strikes the material, a process called recombination takes place that reverts the gas back to its normal state, releasing intense heat. The heat melts the metal and the strong flow of the gas ejects it from the cut. The plasma gasses can be argon, nitrogen, or a mix of argon and hydrogen. They can be replaced by air if a hafnium or zirconium electrode is present. Using compressed air makes this step of the plasma process competitive with the oxy-fuel process of cutting carbon-manganese or stainless steel up to thicknesses of 20mm. In general, inert gases are preferred whenever high-quality cuts are required from reactive alloys.
There are five phases:
Initiation refers to the start of the pilot arc, the moment when the first arc is generated in order to trigger the inflow of gas to the electrode, forcing it out through the gas nozzle.
The second step—main arc generation—involves igniting the arc and making sure that an electric arc has formed between the electrode (the cathode) and the material (the anode). Cutting begins.
As the plasma starts working, the temperature rises and it causes the localized heating that melts the material. Problems may turn up in the nozzle, requiring a cooling system to take place.
Weakened material is ejected using kinetic energy thanks to the plasma jet’s gas flow.
The final arc movement after the material is ejected: the plasma arc moves across the material until the cutting is finished.
Plasma arc cutting is appropriate for a wide range of alloys that are electronically conductive, including carbon steel, stainless steel, and aluminum alloy. It is necessary for the material to form part of the circuit for the plasma arc. If there’s no electrical conductivity, there won’t be a circuit and there won’t be any cutting. Plasma cutting will also work on other metals like titanium, copper, brass, and cast iron, but achieving a quality cutting edge will be more difficult because of the melting temperatures required.
The opening of the nozzle is the only thing that constricts the plasma arc. No secondary medium is deployed. Instead, water or air is used as the coolant.
A secondary medium can be used to constrict the plasma arc further whenever specific characteristics are needed for the metal.
The process of Water Injection Plasma Arc Cutting leads to an improved cut because of a big temperature boost. With water injection, temperatures can go all the way up to 30,000°C.
Speeds are about 10 times faster than oxy-fuel cutting and 100 times faster than laser cutting!
Depending on the series of the machine, they can often be operated simultaneously.
It can be used on any metal that conducts electricity. It can easily cut high-alloy steel, aluminum, and other materials of medium or high thickness. You can even it on high-strength structural steel.
It can be done by handheld devices, lending it portability that doesn’t come with other methods, but it is only as precise as the hold holding it!
It is less expensive than laser or water-jet cutting.
Definitely! Here are a handful:
But, arguably the biggest problem is that it leaves behind a mess called dross, a residue produced by molten metal that sticks to the corners of the finished product and reduces the quality of the cut. In comparison, laser cutting doesn’t produce any dross requiring finishing work. On the other hand, laser cutting is expensive, fixed to its location, and takes up to 100 times longer than plasma cutting.
For materials under 12mm thickness, high tolerance arc cutting (HTPAC) has been an important technological development. It offers higher precision on thinner sheets and products while maintaining its low cost compared to laser cutting.
Kloeckner Metals is proud to offer plate processing capabilities like plasma cutting at our 40+ branches nationwide. Contact us today to get in touch with our thermal and plasma cutting experts.

Steel base plates are fundamental elements employed in various manufacturing...
Metal fabrication is a critical process that transforms raw metal...
The solar industry has undergone a significant transformation by incorporating...
X
The Kloeckner Metals website uses modern technologies. Unfortunately, your browser doesn't support those technologies.
Download the latest version of one of these browsers to experience the site: